This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "Supercell"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(example picture) |
(headers, withmates=1 as default, tab-completion, see also) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
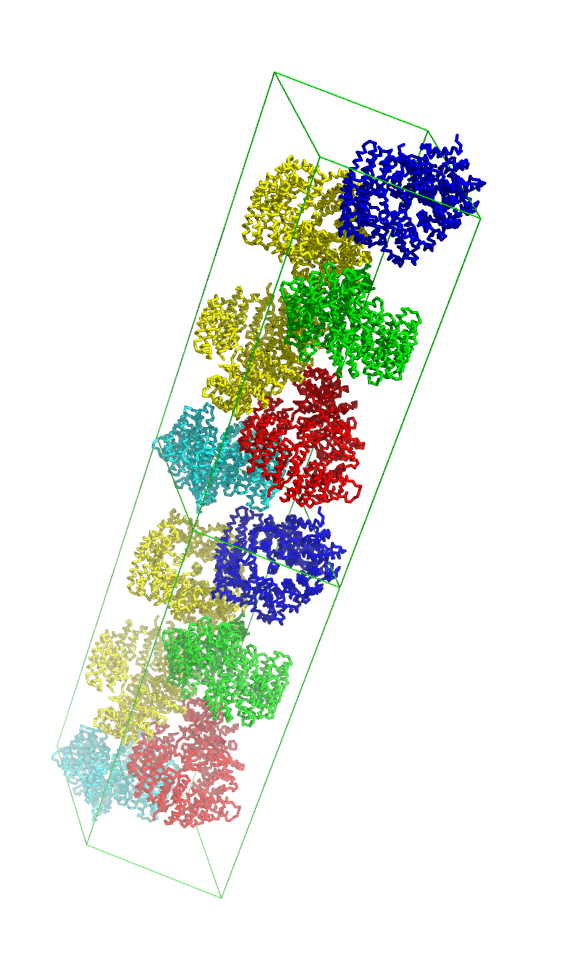
| − | [[File:SupercellExample.png|200px|thumb|right|Example with 2 unit cells in c-direction, created with: supercell 1,1,2,2x19 | + | [[File:SupercellExample.png|200px|thumb|right|Example with 2 unit cells in c-direction, created with: supercell 1,1,2,2x19]] |
| − | + | '''supercell''' can display multiple copies of the unit cell. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Can also fill the unit cell (and its copies) with symmetry mates. | Can also fill the unit cell (and its copies) with symmetry mates. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 8: | ||
Requires [http://numpy.scipy.org numpy]. | Requires [http://numpy.scipy.org numpy]. | ||
| − | = Example = | + | == Example == |
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 15: | ||
supercell 2,1,1, 2x19, green | supercell 2,1,1, 2x19, green | ||
supercell 1,1,2, 2x19, orange, name=super2 | supercell 1,1,2, 2x19, orange, name=super2 | ||
| − | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
| − | = The Code = | + | == The Code == |
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 46: | ||
return basis * edges # numpy.array multiplication! | return basis * edges # numpy.array multiplication! | ||
| − | def supercell(a=1, b=1, c=1, object=None, color='blue', name='supercell', withmates= | + | def supercell(a=1, b=1, c=1, object=None, color='blue', name='supercell', withmates=1): |
''' | ''' | ||
DESCRIPTION | DESCRIPTION | ||
| Line 73: | Line 70: | ||
withmates = bool: also create symmetry mates in displayed cells | withmates = bool: also create symmetry mates in displayed cells | ||
| − | {default: | + | {default: 1} |
SEE ALSO | SEE ALSO | ||
| Line 151: | Line 148: | ||
SEE ALSO | SEE ALSO | ||
| − | symexp | + | symexp, http://www.pymolwiki.org/index.php/SuperSym |
''' | ''' | ||
if object is None: | if object is None: | ||
| Line 191: | Line 188: | ||
cmd.extend('symexpcell', symexpcell) | cmd.extend('symexpcell', symexpcell) | ||
cmd.extend('supercell', supercell) | cmd.extend('supercell', supercell) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # tab-completion of arguments | ||
| + | cmd.auto_arg[3]['supercell'] = [ cmd.object_sc, 'object', ''] | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See Also == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[SuperSym]] | ||
| + | * [[symexp]] | ||
[[Category:Script_Library]] | [[Category:Script_Library]] | ||
[[Category:Math_Scripts]] | [[Category:Math_Scripts]] | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 5 August 2011
supercell can display multiple copies of the unit cell. Can also fill the unit cell (and its copies) with symmetry mates.
See thread on pymol-users mailing list.
Requires numpy.
Example
run supercell.py
fetch 2x19, async=0
supercell 2,1,1, 2x19, green
supercell 1,1,2, 2x19, orange, name=super2
The Code
'''
(c) 2010 Thomas Holder
PyMOL python script (load with `run supercell.py`)
Usage: See "help supercell" and "help symexpcell"
'''
from pymol import cmd, cgo, xray
from math import cos, sin, radians, sqrt
import numpy
def cellbasis(angles, edges):
'''
For the unit cell with given angles and edge lengths calculate the basis
transformation (vectors) as a 4x4 numpy.array
'''
rad = [radians(i) for i in angles]
basis = numpy.identity(4)
basis[0][1] = cos(rad[2])
basis[1][1] = sin(rad[2])
basis[0][2] = cos(rad[1])
basis[1][2] = (cos(rad[0]) - basis[0][1]*basis[0][2])/basis[1][1]
basis[2][2] = sqrt(1 - basis[0][2]**2 - basis[1][2]**2)
edges.append(1.0)
return basis * edges # numpy.array multiplication!
def supercell(a=1, b=1, c=1, object=None, color='blue', name='supercell', withmates=1):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Draw a supercell, as requested by Nicolas Bock on the pymol-users
mailing list (Subject: [PyMOL] feature request: supercell construction
Date: 04/12/2010 10:12:17 PM (Mon, 12 Apr 2010 14:12:17 -0600))
USAGE
supercell a, b, c [, object [, color [, name [, withmates]]]]
ARGUMENTS
a, b, c = integer: repeat cell in x,y,z direction a,b,c times
{default: 1,1,1}
object = string: name of object to take cell definition from
color = string: color of cell {default: blue}
name = string: name of the cgo object to create {default: supercell}
withmates = bool: also create symmetry mates in displayed cells
{default: 1}
SEE ALSO
show cell
'''
if object is None:
object = cmd.get_object_list()[0]
withmates = int(withmates)
sym = cmd.get_symmetry(object)
cell_edges = sym[0:3]
cell_angles = sym[3:6]
basis = cellbasis(cell_angles, cell_edges)
assert isinstance(basis, numpy.ndarray)
ts = list()
for i in range(int(a)):
for j in range(int(b)):
for k in range(int(c)):
ts.append([i,j,k])
obj = [
cgo.BEGIN,
cgo.LINES,
cgo.COLOR,
]
obj.extend(cmd.get_color_tuple(color))
for t in ts:
shift = basis[0:3,0:3] * t
shift = shift[:,0] + shift[:,1] + shift[:,2]
for i in range(3):
vi = basis[0:3,i]
vj = [
numpy.array([0.,0.,0.]),
basis[0:3,(i+1)%3],
basis[0:3,(i+2)%3],
basis[0:3,(i+1)%3] + basis[0:3,(i+2)%3]
]
for j in range(4):
obj.append(cgo.VERTEX)
obj.extend((shift + vj[j]).tolist())
obj.append(cgo.VERTEX)
obj.extend((shift + vj[j] + vi).tolist())
if withmates:
symexpcell('m%d%d%d_' % tuple(t), object, *t)
obj.append(cgo.END)
cmd.delete(name)
cmd.load_cgo(obj, name)
def symexpcell(prefix='mate', object=None, a=0, b=0, c=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Creates all symmetry-related objects for the specified object that
occur with their bounding box center within the unit cell.
USAGE
symexpcell prefix, object, [a, b, c]
ARGUMENTS
prefix = string: prefix of new objects
object = string: object for which to create symmetry mates
a, b, c = integer: create neighboring cell {default: 0,0,0}
SEE ALSO
symexp, http://www.pymolwiki.org/index.php/SuperSym
'''
if object is None:
object = cmd.get_object_list()[0]
sym = cmd.get_symmetry(object)
cell_edges = sym[0:3]
cell_angles = sym[3:6]
spacegroup = sym[6]
basis = cellbasis(cell_angles, cell_edges)
basis = numpy.matrix(basis)
extent = cmd.get_extent(object)
center = sum(numpy.array(extent)) * 0.5
center = numpy.matrix(center.tolist() + [1.0]).T
center_cell = basis.I * center
extra_shift = [[float(i)] for i in (a,b,c)]
i = 0
matrices = xray.sg_sym_to_mat_list(spacegroup)
for mat in matrices:
i += 1
mat = numpy.matrix(mat)
shift = numpy.floor(mat * center_cell)
mat[0:3,3] -= shift[0:3,0]
mat[0:3,3] += extra_shift
mat = basis * mat * basis.I
mat_list = list(mat.flat)
name = '%s%d' % (prefix, i)
cmd.create(name, object)
cmd.transform_object(name, mat_list)
cmd.color(i+1, name)
cmd.extend('symexpcell', symexpcell)
cmd.extend('supercell', supercell)
# tab-completion of arguments
cmd.auto_arg[3]['supercell'] = [ cmd.object_sc, 'object', '']