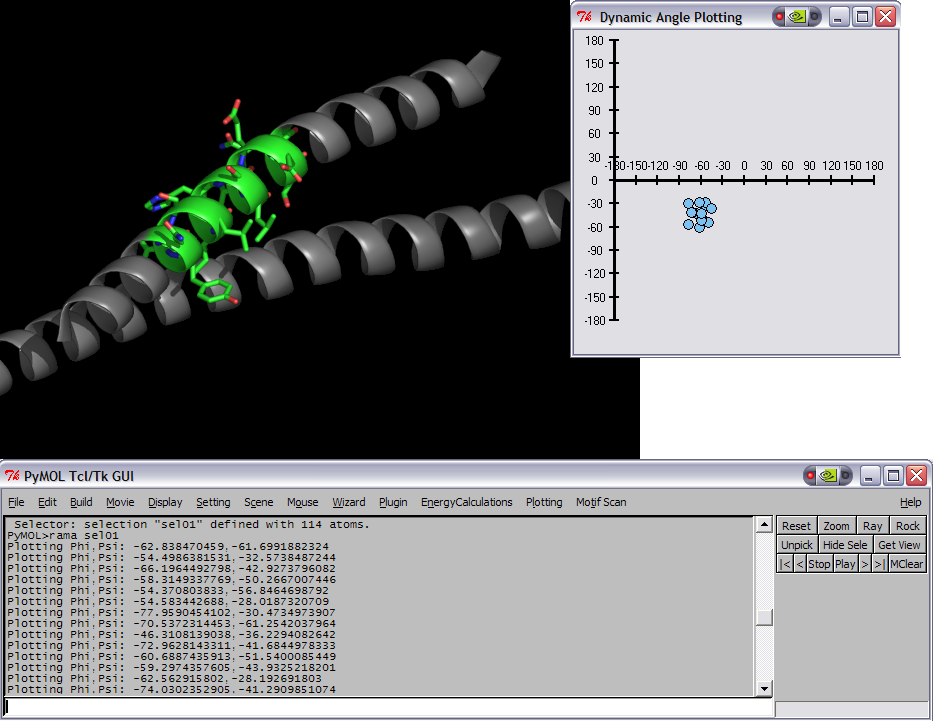
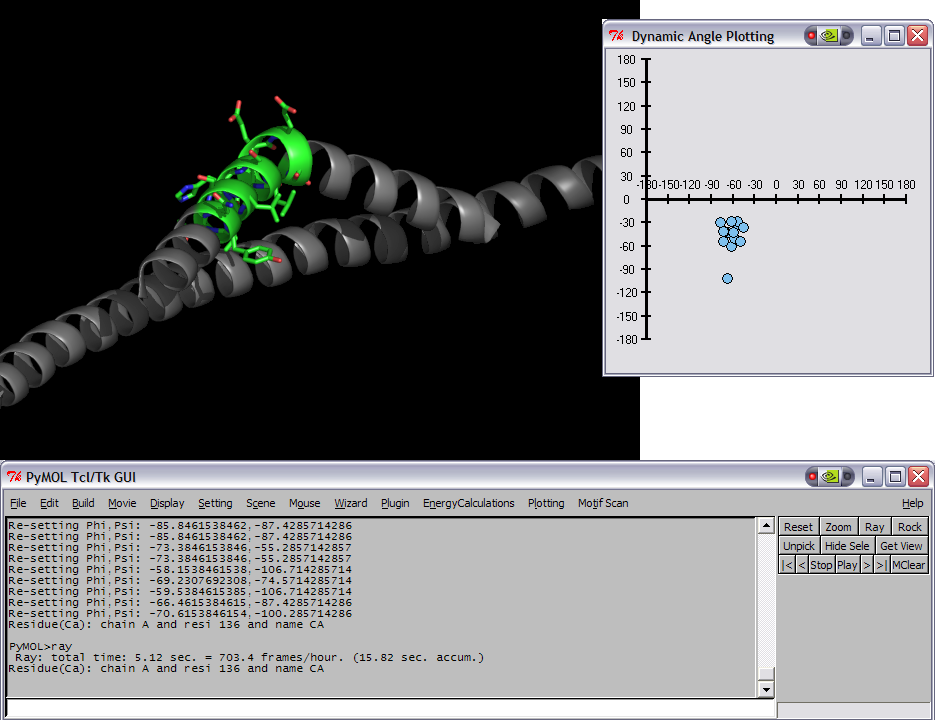
|
|
| Line 41: |
Line 41: |
| | </source> | | </source> |
| | | | |
| − | ===SCRIPTS (DynoPlot.py)=== | + | == Python Code == |
| − | DynoPlot.py
| |
| − | <source lang="python">
| |
| − | ###############################################
| |
| − | # File: DynoPlot.py
| |
| − | # Author: Dan Kulp
| |
| − | # Creation Date: 8/29/05
| |
| − | #
| |
| − | # Modified 2011-11-17 by Thomas Holder
| |
| − | #
| |
| − | # Notes:
| |
| − | # Draw plots that display interactive data.
| |
| − | # Phi,Psi plot shown.
| |
| − | ###############################################
| |
| | | | |
| − | | + | {{Template:PymolScriptRepoDownload|plugins/dynoplot.py}} |
| − | from __future__ import division
| |
| − | from __future__ import generators
| |
| − | | |
| − | import Tkinter
| |
| − | from pymol import cmd
| |
| − | | |
| − | # workaround: Set to True if nothing gets drawn on canvas, for example on linux with "pymol -x"
| |
| − | with_mainloop = False
| |
| − | | |
| − | class SimplePlot(Tkinter.Canvas):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Class variables
| |
| − | mark_size = 4
| |
| − | | |
| − | def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
| |
| − | Tkinter.Canvas.__init__(self, *args, **kwargs)
| |
| − | self.xlabels = [] # axis labels
| |
| − | self.ylabels = []
| |
| − | self.spacingx = 0 # spacing in x direction
| |
| − | self.spacingy = 0
| |
| − | self.xmin = 0 # min value from each axis
| |
| − | self.ymin = 0
| |
| − | self.lastx = 0 # previous x,y pos of mouse
| |
| − | self.lasty = 0
| |
| − | self.isdown = 0 # flag for mouse pressed
| |
| − | self.item = (0,) # items array used for clickable events
| |
| − | self.shapes = {} # store plot data, x,y etc..
| |
| − | self.idx2resn = {} # residue name mapping
| |
| − | self.symbols = 0 # 0: amino acids, 1: secondary structure
| |
| − | | |
| − | def axis(self,xmin=40,xmax=300,ymin=10,ymax=290,xint=290,yint=40,xlabels=[],ylabels=[]):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Store variables in self object
| |
| − | self.xlabels = xlabels
| |
| − | self.ylabels = ylabels
| |
| − | self.spacingx = (xmax-xmin) / (len(xlabels) - 1)
| |
| − | self.spacingy = (ymax-ymin) / (len(ylabels) - 1)
| |
| − | self.xmin = xmin
| |
| − | self.ymin = ymin
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Create axis lines
| |
| − | self.create_line((xmin,xint,xmax,xint),fill="black",width=3)
| |
| − | self.create_line((yint,ymin,yint,ymax),fill="black",width=3)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Create tick marks and labels
| |
| − | nextspot = xmin
| |
| − | for label in xlabels:
| |
| − | self.create_line((nextspot, xint+5,nextspot, xint-5),fill="black",width=2)
| |
| − | self.create_text(nextspot, xint-15, text=label)
| |
| − | if len(xlabels) == 1:
| |
| − | nextspot = xmax
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | nextspot += (xmax - xmin)/ (len(xlabels) - 1)
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | nextspot = ymax
| |
| − | for label in ylabels:
| |
| − | self.create_line((yint+5,nextspot,yint-5,nextspot),fill="black",width=2)
| |
| − | self.create_text(yint-20,nextspot,text=label)
| |
| − | if len(ylabels) == 1:
| |
| − | nextspot = ymin
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | nextspot -= (ymax - ymin)/ (len(ylabels) - 1)
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | # Plot a point
| |
| − | def plot(self,xp,yp,meta):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Convert from 'label' space to 'pixel' space
| |
| − | x = self.convertToPixel("X",xp)
| |
| − | y = self.convertToPixel("Y",yp)
| |
| − | | |
| − | resn, color, ss = self.idx2resn.get(meta)
| |
| − | | |
| − | if self.symbols == 0:
| |
| − | # symbols by amino acid (G/P/other)
| |
| − | mark = {'GLY': 'Tri', 'PRO': 'Rect'}.get(resn, 'Oval')
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | # symbols by secondary structure
| |
| − | mark = {'H': 'Oval', 'S': 'Rect'}.get(ss, 'Tri')
| |
| − | | |
| − | if mark == 'Oval':
| |
| − | create_shape = self.create_oval
| |
| − | coords = [x-self.mark_size, y-self.mark_size,
| |
| − | x+self.mark_size, y+self.mark_size]
| |
| − | elif mark == 'Tri':
| |
| − | create_shape = self.create_polygon
| |
| − | coords = [x, y-self.mark_size,
| |
| − | x+self.mark_size, y+self.mark_size,
| |
| − | x-self.mark_size, y+self.mark_size]
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | create_shape = self.create_rectangle
| |
| − | coords = [x-self.mark_size, y-self.mark_size,
| |
| − | x+self.mark_size, y+self.mark_size]
| |
| − | | |
| − | if color >= 0x40000000:
| |
| − | color = '#%06x' % (color & 0xffffff)
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | color = '#%02x%02x%02x' % tuple([255*i
| |
| − | for i in cmd.get_color_tuple(color)])
| |
| − | | |
| − | oval = create_shape(*coords,
| |
| − | width=1, outline="black", fill=color)
| |
| − | self.shapes[oval] = [x,y,0,xp,yp,meta]
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Convert from pixel space to label space
| |
| − | def convertToLabel(self,axis, value):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Defaultly use X-axis info
| |
| − | label0 = self.xlabels[0]
| |
| − | label1 = self.xlabels[1]
| |
| − | spacing = self.spacingx
| |
| − | min = self.xmin
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Set info for Y-axis use
| |
| − | if axis == "Y":
| |
| − | label0 = self.ylabels[0]
| |
| − | label1 = self.ylabels[1]
| |
| − | spacing = self.spacingy
| |
| − | min = self.ymin
| |
| − | | |
| − | pixel = value - min
| |
| − | label = pixel / spacing
| |
| − | label = label0 + label * abs(label1 - label0)
| |
| − | | |
| − | if axis == "Y":
| |
| − | label = - label
| |
| − | | |
| − | return label
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Converts value from 'label' space to 'pixel' space
| |
| − | def convertToPixel(self,axis, value):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Defaultly use X-axis info
| |
| − | label0 = self.xlabels[0]
| |
| − | label1 = self.xlabels[1]
| |
| − | spacing = self.spacingx
| |
| − | min = self.xmin
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Set info for Y-axis use
| |
| − | if axis == "Y":
| |
| − | label0 = self.ylabels[0]
| |
| − | label1 = self.ylabels[1]
| |
| − | spacing = self.spacingy
| |
| − | min = self.ymin
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Get axis increment in 'label' space
| |
| − | inc = abs(label1 - label0)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # 'Label' difference from value and smallest label (label0)
| |
| − | diff = float(value - label0)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Get whole number in 'label' space
| |
| − | whole = int(diff / inc)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Get fraction number in 'label' space
| |
| − | part = float(float(diff/inc) - whole)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Return 'pixel' position value
| |
| − | pixel = whole * spacing + part * spacing
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Reverse number by subtracting total number of pixels - value pixels
| |
| − | if axis == "Y":
| |
| − | tot_label_diff = float(self.ylabels[-1] - label0)
| |
| − | tot_label_whole = int(tot_label_diff / inc)
| |
| − | tot_label_part = float(float(tot_label_diff / inc) - tot_label_whole)
| |
| − | tot_label_pix = tot_label_whole * spacing + tot_label_part *spacing
| |
| − | | |
| − | pixel = tot_label_pix - pixel
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Add min edge pixels
| |
| − | pixel = pixel + min
| |
| − | | |
| − | return pixel
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | # Print out which data point you just clicked on..
| |
| − | def pickWhich(self,event):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Find closest data point
| |
| − | x = event.widget.canvasx(event.x)
| |
| − | y = event.widget.canvasx(event.y)
| |
| − | spot = event.widget.find_closest(x,y)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Print the shape's meta information corresponding with the shape that was picked
| |
| − | if spot[0] in self.shapes:
| |
| − | cmd.select('sele', '(%s`%d)' % self.shapes[spot[0]][5])
| |
| − | cmd.iterate('sele', 'print " You clicked /%s/%s/%s/%s`%s/%s (DynoPlot)" %' + \
| |
| − | ' (model, segi, chain, resn, resi, name)')
| |
| − | cmd.center('byres sele', animate=1)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Mouse Down Event
| |
| − | def down(self,event):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Store x,y position
| |
| − | self.lastx = event.x
| |
| − | self.lasty = event.y
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Find the currently selected item
| |
| − | x = event.widget.canvasx(event.x)
| |
| − | y = event.widget.canvasx(event.y)
| |
| − | self.item = event.widget.find_closest(x,y)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Identify that the mouse is down
| |
| − | self.isdown = 1
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Mouse Up Event
| |
| − | def up(self,event):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Get label space version of x,y
| |
| − | labelx = self.convertToLabel("X",event.x)
| |
| − | labely = self.convertToLabel("Y",event.y)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Convert new position into label space..
| |
| − | if self.item[0] in self.shapes:
| |
| − | self.shapes[self.item[0]][0] = event.x
| |
| − | self.shapes[self.item[0]][1] = event.y
| |
| − | self.shapes[self.item[0]][2] = 1
| |
| − | self.shapes[self.item[0]][3] = labelx
| |
| − | self.shapes[self.item[0]][4] = labely
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Reset Flags
| |
| − | self.item = (0,)
| |
| − | self.isdown = 0
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Mouse Drag(Move) Event
| |
| − | def drag(self,event):
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Check that mouse is down and item clicked is a valid data point
| |
| − | if self.isdown and self.item[0] in self.shapes:
| |
| − | | |
| − | self.move(self.item, event.x - self.lastx, event.y - self.lasty)
| |
| − | | |
| − | self.lastx = event.x
| |
| − | self.lasty = event.y
| |
| − | | |
| − | def set_phipsi(model, index, phi, psi):
| |
| − | atsele = [
| |
| − | 'first ((%s`%d) extend 2 and name C)' % (model, index), # prev C
| |
| − | 'first ((%s`%d) extend 1 and name N)' % (model, index), # this N
| |
| − | '(%s`%d)' % (model, index), # this CA
| |
| − | 'last ((%s`%d) extend 1 and name C)' % (model, index), # this C
| |
| − | 'last ((%s`%d) extend 2 and name N)' % (model, index), # next N
| |
| − | ]
| |
| − | try:
| |
| − | cmd.set_dihedral(atsele[0], atsele[1], atsele[2], atsele[3], phi)
| |
| − | cmd.set_dihedral(atsele[1], atsele[2], atsele[3], atsele[4], psi)
| |
| − | except:
| |
| − | print ' DynoPlot Error: cmd.set_dihedral failed'
| |
| − | | |
| − | # New Callback object, so that we can update the structure when phi,psi points are moved.
| |
| − | class DynoRamaObject:
| |
| − | def __init__(self, selection=None, name=None, symbols=''):
| |
| − | from pymol import _ext_gui as pmgapp
| |
| − | if pmgapp is not None:
| |
| − | import Pmw
| |
| − | rootframe = Pmw.MegaToplevel(pmgapp.root)
| |
| − | parent = rootframe.interior()
| |
| − | else:
| |
| − | rootframe = Tkinter.Tk()
| |
| − | parent = rootframe
| |
| − | | |
| − | rootframe.title(' Dynamic Angle Plotting ')
| |
| − | rootframe.protocol("WM_DELETE_WINDOW", self.close_callback)
| |
| − | | |
| − | canvas = SimplePlot(parent,width=320,height=320)
| |
| − | canvas.bind("<Button-2>",canvas.pickWhich)
| |
| − | canvas.bind("<Button-3>",canvas.pickWhich)
| |
| − | canvas.pack(side=Tkinter.LEFT,fill="both",expand=1)
| |
| − | canvas.axis(xint=150,
| |
| − | xlabels=[-180,-120,-60,0,60,120,180],
| |
| − | ylabels=[-180,-150,-120,-90,-60,-30,0,30,60,90,120,150,180])
| |
| − | canvas.update()
| |
| − | | |
| − | if symbols == 'ss':
| |
| − | canvas.symbols = 1
| |
| − | | |
| − | if name is None:
| |
| − | try:
| |
| − | name = cmd.get_unused_name('DynoRama')
| |
| − | except AttributeError:
| |
| − | name = 'DynoRamaObject'
| |
| − | | |
| − | self.rootframe = rootframe
| |
| − | self.canvas = canvas
| |
| − | self.name = name
| |
| − | self.lock = 0
| |
| − | | |
| − | if name != 'none':
| |
| − | auto_zoom = cmd.get('auto_zoom')
| |
| − | cmd.set('auto_zoom', 0)
| |
| − | cmd.load_callback(self, name)
| |
| − | cmd.set('auto_zoom', auto_zoom)
| |
| − | canvas.bind("<ButtonPress-1>",canvas.down)
| |
| − | canvas.bind("<ButtonRelease-1>",canvas.up)
| |
| − | canvas.bind("<Motion>",canvas.drag)
| |
| − | | |
| − | if selection is not None:
| |
| − | self.start(selection)
| |
| − | | |
| − | if with_mainloop and pmgapp is None:
| |
| − | rootframe.mainloop()
| |
| − | | |
| − | def close_callback(self):
| |
| − | cmd.delete(self.name)
| |
| − | self.rootframe.destroy()
| |
| − | | |
| − | def start(self,sel):
| |
| − | self.lock = 1
| |
| − | cmd.iterate('(%s) and name CA' % sel,'idx2resn[model,index] = (resn, color, ss)',
| |
| − | space={'idx2resn': self.canvas.idx2resn})
| |
| − | for model_index, (phi,psi) in cmd.get_phipsi(sel).iteritems():
| |
| − | print " Plotting Phi,Psi: %8.2f,%8.2f" % (phi, psi)
| |
| − | self.canvas.plot(phi, psi, model_index)
| |
| − | self.lock = 0
| |
| − | | |
| − | def __call__(self):
| |
| − | if self.lock:
| |
| − | return
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Loop through each item on plot to see if updated
| |
| − | for value in self.canvas.shapes.itervalues():
| |
| − | # Look for update flag...
| |
| − | if value[2]:
| |
| − | # Set residue's phi,psi to new values
| |
| − | model, index = value[5]
| |
| − | print " Re-setting Phi,Psi: %8.2f,%8.2f" % (value[3],value[4])
| |
| − | set_phipsi(model, index, value[3], value[4])
| |
| − | value[2] = 0
| |
| − | | |
| − | def rama(sel='(all)', name=None, symbols='aa', filename=None):
| |
| − | '''
| |
| − | DESCRIPTION
| |
| − | | |
| − | Ramachandran Plot
| |
| − | http://pymolwiki.org/index.php/DynoPlot
| |
| − | | |
| − | ARGUMENTS
| |
| − | | |
| − | sel = string: atom selection {default: all}
| |
| − | | |
| − | name = string: name of callback object which is responsible for setting
| |
| − | angles when canvas points are dragged, or 'none' to not create a callback
| |
| − | object {default: DynoRamaObject}
| |
| − | | |
| − | symbols = string: aa for amino acid or ss for secondary structure {default: aa}
| |
| − | | |
| − | filename = string: filename for postscript dump of canvas {default: None}
| |
| − | '''
| |
| − | dyno = DynoRamaObject(sel, name, symbols)
| |
| − | if filename is not None:
| |
| − | dyno.canvas.postscript(file=filename)
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Extend these commands
| |
| − | cmd.extend('ramachandran', rama)
| |
| − | cmd.auto_arg[0]['ramachandran'] = cmd.auto_arg[0]['zoom']
| |
| − | | |
| − | # Add to plugin menu
| |
| − | def __init_plugin__(self):
| |
| − | self.menuBar.addcascademenu('Plugin', 'PlotTools', 'Plot Tools', label='Plot Tools')
| |
| − | self.menuBar.addmenuitem('PlotTools', 'command', 'Launch Rama Plot', label='Rama Plot',
| |
| − | command = lambda: DynoRamaObject('(enabled)'))
| |
| − | | |
| − | # vi:expandtab:smarttab
| |
| − | </source>
| |
| | | | |
| | ===ADDITIONAL RESOURCES=== | | ===ADDITIONAL RESOURCES=== |