This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "Color By Mutations"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (2 revisions) |
(Python 3) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
# return red for residues that are not part of the 20 amino acids | # return red for residues that are not part of the 20 amino acids | ||
if aa1 not in aa_3l or aa2 not in aa_3l: | if aa1 not in aa_3l or aa2 not in aa_3l: | ||
| − | + | return 'red' | |
# if the two are the same, return blue | # if the two are the same, return blue | ||
if aa1 == aa2: | if aa1 == aa2: | ||
| − | + | return 'blue' | |
i1 = aa_3l[aa1] | i1 = aa_3l[aa1] | ||
i2 = aa_3l[aa2] | i2 = aa_3l[aa2] | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
colvec = [(0., 0., 1.), (1.,0.,0.)] | colvec = [(0., 0., 1.), (1.,0.,0.)] | ||
bcolor = (1.-b, 0., b) | bcolor = (1.-b, 0., b) | ||
| − | col_name = '0x%02x%02x%02x'%( | + | col_name = '0x%02x%02x%02x' % tuple(int(b * 0xFF) for b in bcolor) |
return col_name | return col_name | ||
| Line 121: | Line 121: | ||
if cmd.count_atoms(obj1) == 0: | if cmd.count_atoms(obj1) == 0: | ||
| − | print '%s is empty'%obj1 | + | print('%s is empty'%obj1) |
return | return | ||
if cmd.count_atoms(obj2) == 0: | if cmd.count_atoms(obj2) == 0: | ||
| − | print '%s is empty'%obj2 | + | print('%s is empty'%obj2) |
return | return | ||
waters = int(waters) | waters = int(waters) | ||
| Line 178: | Line 178: | ||
if mutant_selection == '': | if mutant_selection == '': | ||
| − | + | raise CmdException('No mutations found') | |
| − | |||
# create selections | # create selections | ||
| Line 206: | Line 205: | ||
cmd.color('red', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj1) | cmd.color('red', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj1) | ||
cmd.color('salmon', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj2) | cmd.color('salmon', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj2) | ||
| − | print ''' | + | print(''' |
Mutations are highlighted in blue and red. | Mutations are highlighted in blue and red. | ||
All mutated sidechains of %s are colored blue, the corresponding ones from %s are | All mutated sidechains of %s are colored blue, the corresponding ones from %s are | ||
| Line 213: | Line 212: | ||
Aligned regions without mutations are colored white. | Aligned regions without mutations are colored white. | ||
Regions not used for the alignment are gray. | Regions not used for the alignment are gray. | ||
| − | NOTE: There could be mutations in the gray regions that were not detected.'''%(obj1, obj2) | + | NOTE: There could be mutations in the gray regions that were not detected.'''%(obj1, obj2)) |
cmd.delete(aln) | cmd.delete(aln) | ||
cmd.deselect() | cmd.deselect() | ||
Revision as of 06:52, 20 June 2020
This script creates an alignment of two proteins and superimposes them. Aligned residues that are different in the two (i.e. mutations) are highlighted and colored according to their difference in the BLOSUM90 matrix. It is meant to be used for similar proteins, e.g. close homologs or point mutants, to visualize their differences.
Example
color_by_mutation protein1, protein2
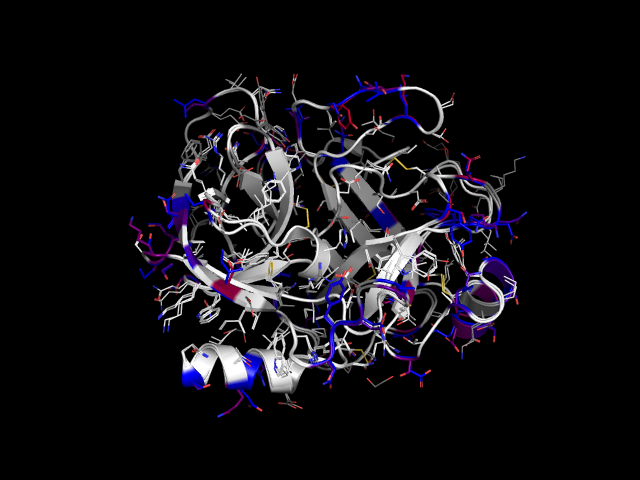
Example: rat trypsin and cow trypsin colored by color_by_mutation.
'''
created by Christoph Malisi.
Creates an alignment of two proteins and superimposes them.
Aligned residues that are different in the two (i.e. mutations) are highlighted and
colored according to their difference in the BLOSUM90 matrix.
Is meant to be used for similar proteins, e.g. close homologs or point mutants,
to visualize their differences.
'''
from pymol import cmd
aa_3l = {'ALA':0, 'ARG':1, 'ASN':2, 'ASP':3, 'CYS':4, 'GLN':5, 'GLU':6, 'GLY':7, 'HIS':8, 'ILE':9, 'LEU':10, 'LYS':11,
'MET':12, 'PHE':13, 'PRO':14, 'SER':15, 'THR':16, 'TRP':17, 'TYR':18, 'VAL':19, 'B':20, 'Z':21, 'X':22, '*':23}
# A R N D C Q E G H I L K M F P S T W Y V B Z X *
blosum90 = [[ 5, -2, -2, -3, -1, -1, -1, 0, -2, -2, -2, -1, -2, -3, -1, 1, 0, -4, -3, -1, -2, -1, -1, -6],
[-2, 6, -1, -3, -5, 1, -1, -3, 0, -4, -3, 2, -2, -4, -3, -1, -2, -4, -3, -3, -2, 0, -2, -6],
[-2, -1, 7, 1, -4, 0, -1, -1, 0, -4, -4, 0, -3, -4, -3, 0, 0, -5, -3, -4, 4, -1, -2, -6],
[-3, -3, 1, 7, -5, -1, 1, -2, -2, -5, -5, -1, -4, -5, -3, -1, -2, -6, -4, -5, 4, 0, -2, -6],
[-1, -5, -4, -5, 9, -4, -6, -4, -5, -2, -2, -4, -2, -3, -4, -2, -2, -4, -4, -2, -4, -5, -3, -6],
[-1, 1, 0, -1, -4, 7, 2, -3, 1, -4, -3, 1, 0, -4, -2, -1, -1, -3, -3, -3, -1, 4, -1, -6],
[-1, -1, -1, 1, -6, 2, 6, -3, -1, -4, -4, 0, -3, -5, -2, -1, -1, -5, -4, -3, 0, 4, -2, -6],
[ 0, -3, -1, -2, -4, -3, -3, 6, -3, -5, -5, -2, -4, -5, -3, -1, -3, -4, -5, -5, -2, -3, -2, -6],
[-2, 0, 0, -2, -5, 1, -1, -3, 8, -4, -4, -1, -3, -2, -3, -2, -2, -3, 1, -4, -1, 0, -2, -6],
[-2, -4, -4, -5, -2, -4, -4, -5, -4, 5, 1, -4, 1, -1, -4, -3, -1, -4, -2, 3, -5, -4, -2, -6],
[-2, -3, -4, -5, -2, -3, -4, -5, -4, 1, 5, -3, 2, 0, -4, -3, -2, -3, -2, 0, -5, -4, -2, -6],
[-1, 2, 0, -1, -4, 1, 0, -2, -1, -4, -3, 6, -2, -4, -2, -1, -1, -5, -3, -3, -1, 1, -1, -6],
[-2, -2, -3, -4, -2, 0, -3, -4, -3, 1, 2, -2, 7, -1, -3, -2, -1, -2, -2, 0, -4, -2, -1, -6],
[-3, -4, -4, -5, -3, -4, -5, -5, -2, -1, 0, -4, -1, 7, -4, -3, -3, 0, 3, -2, -4, -4, -2, -6],
[-1, -3, -3, -3, -4, -2, -2, -3, -3, -4, -4, -2, -3, -4, 8, -2, -2, -5, -4, -3, -3, -2, -2, -6],
[ 1, -1, 0, -1, -2, -1, -1, -1, -2, -3, -3, -1, -2, -3, -2, 5, 1, -4, -3, -2, 0, -1, -1, -6],
[ 0, -2, 0, -2, -2, -1, -1, -3, -2, -1, -2, -1, -1, -3, -2, 1, 6, -4, -2, -1, -1, -1, -1, -6],
[-4, -4, -5, -6, -4, -3, -5, -4, -3, -4, -3, -5, -2, 0, -5, -4, -4, 11, 2, -3, -6, -4, -3, -6],
[-3, -3, -3, -4, -4, -3, -4, -5, 1, -2, -2, -3, -2, 3, -4, -3, -2, 2, 8, -3, -4, -3, -2, -6],
[-1, -3, -4, -5, -2, -3, -3, -5, -4, 3, 0, -3, 0, -2, -3, -2, -1, -3, -3, 5, -4, -3, -2, -6],
[-2, -2, 4, 4, -4, -1, 0, -2, -1, -5, -5, -1, -4, -4, -3, 0, -1, -6, -4, -4, 4, 0, -2, -6],
[-1, 0, -1, 0, -5, 4, 4, -3, 0, -4, -4, 1, -2, -4, -2, -1, -1, -4, -3, -3, 0, 4, -1, -6],
[-1, -2, -2, -2, -3, -1, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -1, -1, -2, -2, -1, -1, -3, -2, -2, -2, -1, -2, -6],
[-6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, 1]]
def getBlosum90ColorName(aa1, aa2):
'''returns a rgb color name of a color that represents the similarity of the two residues according to
the BLOSUM90 matrix. the color is on a spectrum from blue to red, where blue is very similar, and
red very disimilar.'''
# return red for residues that are not part of the 20 amino acids
if aa1 not in aa_3l or aa2 not in aa_3l:
return 'red'
# if the two are the same, return blue
if aa1 == aa2:
return 'blue'
i1 = aa_3l[aa1]
i2 = aa_3l[aa2]
b = blosum90[i1][i2]
# 3 is the highest score for non-identical substitutions, so substract 4 to get into range [-10, -1]
b = abs(b - 4)
# map to (0, 1]:
b = 1. - (b / 10.0)
# red = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], blue = [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
colvec = [(0., 0., 1.), (1.,0.,0.)]
bcolor = (1.-b, 0., b)
col_name = '0x%02x%02x%02x' % tuple(int(b * 0xFF) for b in bcolor)
return col_name
def color_by_mutation(obj1, obj2, waters=0, labels=0):
'''
DESCRIPTION
Creates an alignment of two proteins and superimposes them.
Aligned residues that are different in the two (i.e. mutations) are highlighted and
colored according to their difference in the BLOSUM90 matrix.
Is meant to be used for similar proteins, e.g. close homologs or point mutants,
to visualize their differences.
USAGE
color_by_mutation selection1, selection2 [,waters [,labels ]]
ARGUMENTS
obj1: object or selection
obj2: object or selection
waters: bool (0 or 1). If 1, waters are included in the view, colored
differently for the both input structures.
default = 0
labels: bool (0 or 1). If 1, the possibly mutated sidechains are
labeled by their chain, name and id
default = 0
EXAMPLE
color_by_mutation protein1, protein2
SEE ALSO
super
'''
from pymol import stored, CmdException
if cmd.count_atoms(obj1) == 0:
print('%s is empty'%obj1)
return
if cmd.count_atoms(obj2) == 0:
print('%s is empty'%obj2)
return
waters = int(waters)
labels = int(labels)
# align the two proteins
aln = '__aln'
# first, an alignment with 0 cycles (no atoms are rejected, which maximized the number of aligned residues)
# for some mutations in the same protein this works fine). This is essentially done to get a
# sequence alignment
cmd.super(obj1, obj2, object=aln, cycles=0)
# superimpose the the object using the default parameters to get a slightly better superimposition,
# i.e. get the best structural alignment
cmd.super(obj1, obj2)
stored.resn1, stored.resn2 = [], []
stored.resi1, stored.resi2 = [], []
stored.chain1, stored.chain2 = [], []
# store residue ids, residue names and chains of aligned residues
cmd.iterate(obj1 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.resn1.append(resn)')
cmd.iterate(obj2 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.resn2.append(resn)')
cmd.iterate(obj1 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.resi1.append(resi)')
cmd.iterate(obj2 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.resi2.append(resi)')
cmd.iterate(obj1 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.chain1.append(chain)')
cmd.iterate(obj2 + ' and name CA and ' + aln, 'stored.chain2.append(chain)')
mutant_selection = ''
non_mutant_selection = 'none or '
colors = []
# loop over the aligned residues
for n1, n2, i1, i2, c1, c2 in zip(stored.resn1, stored.resn2,
stored.resi1, stored.resi2,
stored.chain1, stored.chain2):
# take care of 'empty' chain names
if c1 == '':
c1 = '""'
if c2 == '':
c2 = '""'
if n1 == n2:
non_mutant_selection += '((%s and resi %s and chain %s) or (%s and resi %s and chain %s)) or '%(obj1, i1, c1, obj2, i2, c2 )
else:
mutant_selection += '((%s and resi %s and chain %s) or (%s and resi %s and chain %s)) or '%(obj1, i1, c1, obj2, i2, c2 )
# get the similarity (according to the blosum matrix) of the two residues and
c = getBlosum90ColorName(n1, n2)
colors.append((c, '%s and resi %s and chain %s and elem C'%(obj2, i2, c2)))
if mutant_selection == '':
raise CmdException('No mutations found')
# create selections
cmd.select('mutations', mutant_selection[:-4])
cmd.select('non_mutations', non_mutant_selection[:-4])
cmd.select('not_aligned', '(%s or %s) and not mutations and not non_mutations'%(obj1, obj2))
# create the view and coloring
cmd.hide('everything', '%s or %s'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.show('cartoon', '%s or %s'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.show('lines', '(%s or %s) and ((non_mutations or not_aligned) and not name c+o+n)'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.show('sticks', '(%s or %s) and mutations and not name c+o+n'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.color('gray', 'elem C and not_aligned')
cmd.color('white', 'elem C and non_mutations')
cmd.color('blue', 'elem C and mutations and %s'%obj1)
for (col, sel) in colors:
cmd.color(col, sel)
cmd.hide('everything', '(hydro) and (%s or %s)'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.center('%s or %s'%(obj1, obj2))
if labels:
cmd.label('mutations and name CA','"(%s-%s-%s)"%(chain, resi, resn)')
if waters:
cmd.set('sphere_scale', '0.1')
cmd.show('spheres', 'resn HOH and (%s or %s)'%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.color('red', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj1)
cmd.color('salmon', 'resn HOH and %s'%obj2)
print('''
Mutations are highlighted in blue and red.
All mutated sidechains of %s are colored blue, the corresponding ones from %s are
colored on a spectrum from blue to red according to how similar the two amino acids are
(as measured by the BLOSUM90 substitution matrix).
Aligned regions without mutations are colored white.
Regions not used for the alignment are gray.
NOTE: There could be mutations in the gray regions that were not detected.'''%(obj1, obj2))
cmd.delete(aln)
cmd.deselect()
cmd.extend("color_by_mutation", color_by_mutation)