This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "Wfmesh"
Cowsandmilk (talk | contribs) (Undo revision 8034 by Cowsandmilk (Talk)) |
Cowsandmilk (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
# Create openGL objects from a wavefront (obj) file | # Create openGL objects from a wavefront (obj) file | ||
############################################### | ############################################### | ||
| − | + | ||
import os | import os | ||
import re | import re | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
from pymol.opengl.gl import * | from pymol.opengl.gl import * | ||
from pymol.callback import Callback | from pymol.callback import Callback | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
# Wrapper Function, to create a given WFObj with a specific name (flip = 1 if OpenFX + Crossroads used) | # Wrapper Function, to create a given WFObj with a specific name (flip = 1 if OpenFX + Crossroads used) | ||
def createWFObj(file, name,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0): | def createWFObj(file, name,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0): | ||
| − | + | obj = WFMesh(file,translate,flip) | |
| − | + | cmd.load_callback(obj,name) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
# Class for Wavefront Mesh | # Class for Wavefront Mesh | ||
class WFMesh(Callback): | class WFMesh(Callback): | ||
| − | + | ||
verts = [] # list of vertices | verts = [] # list of vertices | ||
polys = [] # list of poylgons | polys = [] # list of poylgons | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
vavenorms = [] # list of vertex normals, redundant -- I'm far froma python pro. | vavenorms = [] # list of vertex normals, redundant -- I'm far froma python pro. | ||
sections = {} # list of sections of mesh | sections = {} # list of sections of mesh | ||
| − | + | ||
# Read mesh into memory | # Read mesh into memory | ||
def readOBJ(self,file): | def readOBJ(self,file): | ||
if os.path.exists(file): | if os.path.exists(file): | ||
| − | + | input = open(file,'r') | |
| − | + | for line in input: | |
| − | + | dat = re.split("\s+", line) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Find vertex line | |
| − | + | if line[0] == 'v' and line[1] != 't' and line[1] != 'n': self.verts.append([dat[1],dat[2],dat[3]]) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Find polygon line | |
| − | + | if line[0] == 'f': self.polys.append([dat[1],dat[2],dat[3]]) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Find section line | |
| − | + | if line[0] == 'g': self.sections[len(self.polys)] = dat[1] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | # Compute the normals for each polygon and each vertex | + | # Compute the normals for each polygon and each vertex |
def computeNorms(self): | def computeNorms(self): | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Compute norms for each polygon | |
| − | + | for p in self.polys: | |
| − | + | v12 = [float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][0]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][0]),\ | |
| − | + | float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][1]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][1]),\ | |
| − | + | float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][2]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][2]) \ | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | v13 = [float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][0]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][0]),\ | |
| − | + | float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][1]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][1]),\ | |
| − | + | float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][2]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][2]) \ | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Compute poly normal | |
| − | + | polynorm = self.cross(v12,v13) | |
| − | + | norm = self.normalize(polynorm) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Files created by OpenFX, Crossroads combination need have their normals flipped | |
| − | + | if self.flip: | |
| − | + | norm[0] = -norm[0] | |
| − | + | norm[1] = -norm[1] | |
| − | + | norm[2] = -norm[2] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Append poly norm to polygonal norm array | |
| − | + | self.pnorms.append(norm) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Add norm to each vertexes norm.. | |
| − | + | try: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][0]) + norm[0], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][1]) + norm[1], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][2]) + norm[2] | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | except: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | try: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][0]) + norm[0], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][1]) + norm[1], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][2]) + norm[2] | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | except: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | try: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[2])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][0]) + norm[0], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][1]) + norm[1], | |
| − | + | float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][2]) + norm[2] | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | except: | |
| − | + | self.vnorms[int(p[2])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
# Average out each vnorm.. | # Average out each vnorm.. | ||
| − | + | index = 0 | |
| − | + | for v in self.vnorms.values(): | |
| − | + | self.vavenorms.append([v[0]/4, v[1]/4, v[2]/4]) | |
| − | + | index += 1 | |
| − | + | ||
# Utility function to normalize a given vector | # Utility function to normalize a given vector | ||
def normalize(self,v): | def normalize(self,v): | ||
| − | + | mag = v[0]*v[0]+v[1]*v[1]+v[2]*v[2] | |
| − | + | if mag <= 0: | |
| − | + | mag = 1 | |
| − | + | else: | |
| − | + | mag = math.sqrt(mag) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | return [v[0]/mag, v[1]/mag,v[2]/mag] | |
| − | + | ||
# Utility cross product function | # Utility cross product function | ||
def cross(self,v1,v2): | def cross(self,v1,v2): | ||
| − | + | x = 0 | |
| − | + | y = 1 | |
| − | + | z = 2 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | return [v1[y]*v2[z] - v1[z]*v2[y],\ | |
| − | + | v1[z]*v2[x] - v1[x]*v2[z],\ | |
| − | + | v1[x]*v2[y] - v1[y]*v2[x] | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | + | ||
# Constructor | # Constructor | ||
def __init__(self, file,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0): | def __init__(self, file,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0): | ||
| Line 191: | Line 191: | ||
self.vnorms = {} | self.vnorms = {} | ||
self.vavenorms = [] | self.vavenorms = [] | ||
| − | + | self.translate = translate | |
| − | + | self.flip = flip | |
| − | + | ||
print "Read in file: "+str(file) | print "Read in file: "+str(file) | ||
| − | + | self.readOBJ(file) | |
| − | + | print "Done reading in WFMesh, now compute norms" | |
| − | + | self.computeNorms() | |
| − | + | print "Done computing norms, now display WFMesh" | |
| − | + | ||
# Draw Function | # Draw Function | ||
def __call__(self): | def __call__(self): | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | glColorMaterial(GL_FRONT, GL_DIFFUSE); | |
glEnable(GL_COLOR_MATERIAL); | glEnable(GL_COLOR_MATERIAL); | ||
| − | + | glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Color Everything grey | |
glColor3f(0.5,0.5,0.5); | glColor3f(0.5,0.5,0.5); | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | index = 0 | |
| − | + | glPushMatrix() | |
| − | + | glTranslated(self.translate[0],self.translate[1],self.translate[2]) | |
| − | + | for p in self.polys: | |
| − | + | glBegin(GL_POLYGON) | |
| − | + | glNormal3f(float(self.pnorms[index][0]),float(self.pnorms[index][1]),float(self.pnorms[index][2])) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | for i in range(0,len(p)): | |
| − | + | glVertex3f(float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][0]),float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][1]),float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][2])) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | # Vertex Normals - not computed correctly, so commented out for now | |
| − | # | + | # norm = self.vnorms[int(p[i])-1] |
| − | # | + | # glNormal3f(float(norm[0]),float(norm[1]),float(norm[2])) |
| − | + | glEnd() | |
| − | + | index += 1 | |
| − | + | glPopMatrix() | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
cmd.extend("createWFObj", createWFObj) | cmd.extend("createWFObj", createWFObj) | ||
| − | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
Revision as of 19:10, 14 February 2010
DESCRIPTION
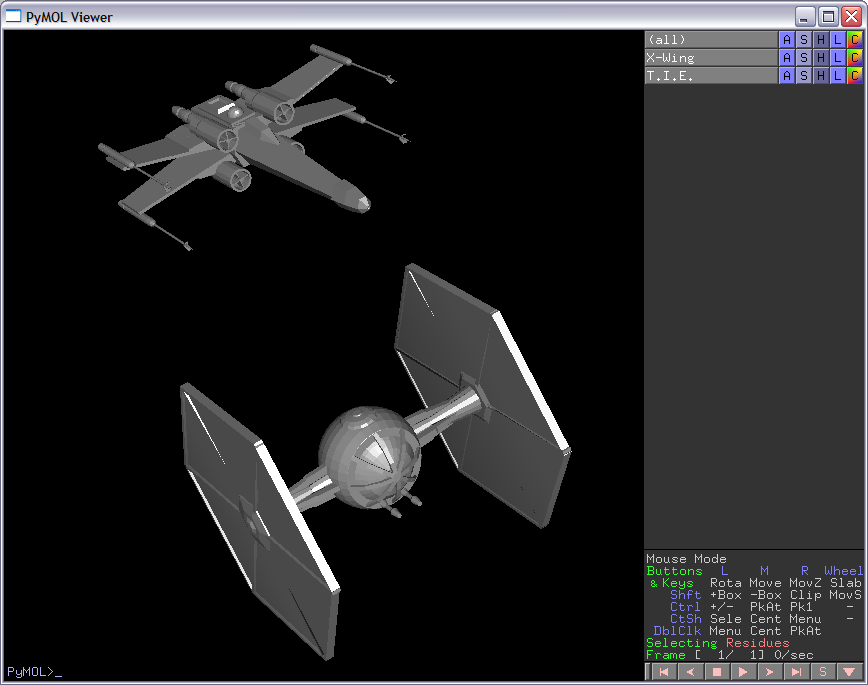
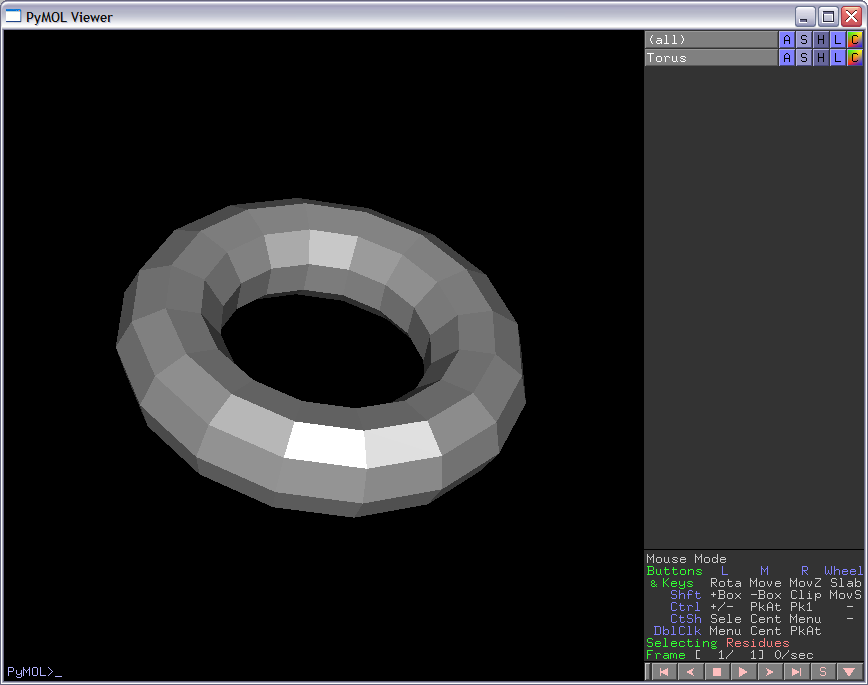
This script will create an object for any Wavefront(.OBJ) mesh file. This is a way to extend the number of objects you can use. Also, you have more control over the coloring, transformations, etc than the CGOs. Although there are a number of these obj files on the web, you can also easily created them with open source tools (OpenFX, Crossroads3D). It takes literally, 2 min to get an object created and then loaded into pymol. Simply open OpenFX Designer, click File->Insert->Model, then choose any of the models (or create your own of course!), then export it as .3ds file. Then open the .3ds file from Crossroads3D and export as Wavefront OBJ.
- createWFMesh - create a mesh object from Wavefront (*.obj) formated file
IMAGES
SETUP
Simply "run WFMesh.py"
NOTES / STATUS
- Tested on Pymolv0.97, Windows platform, should work on linux as well.
- Coloring is fixed for grey and sections of mesh are stored, but not used.
- Simple opengl calls; not optimized (display lists, etc) or anything.
- Vertex Normal code is broken, so normals are per polygon right now.
- Post problems in the discussion page, on 'my talk' page or just email me : dwkulp@mail.med.upenn.edu
USAGE
createWFObj file, name [,translate=[0,0,0]] [,flip=0]
EXAMPLES
createWFObj "ship.obj" "Ship" createWFObj "torus.obj" "Torus" flip=1 # Flip = 1, if OBJ created by openFX, crossroads3D combination createWFObj "torus.obj" "Torus" translate=[10,10,0] flip=1
REFERENCES
SCRIPTS (WFMesh.py)
WFMesh.py
###############################################
# File: WFObj.py
# Author: Dan Kulp
# Creation Date: 5/13/05
#
# Notes:
# Create openGL objects from a wavefront (obj) file
###############################################
import os
import re
import math
from pymol.opengl.gl import *
from pymol.callback import Callback
# Wrapper Function, to create a given WFObj with a specific name (flip = 1 if OpenFX + Crossroads used)
def createWFObj(file, name,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0):
obj = WFMesh(file,translate,flip)
cmd.load_callback(obj,name)
# Class for Wavefront Mesh
class WFMesh(Callback):
verts = [] # list of vertices
polys = [] # list of poylgons
pnorms = [] # list of polynomal normals
vnorms = {} # dict. of vertex normals
vavenorms = [] # list of vertex normals, redundant -- I'm far froma python pro.
sections = {} # list of sections of mesh
# Read mesh into memory
def readOBJ(self,file):
if os.path.exists(file):
input = open(file,'r')
for line in input:
dat = re.split("\s+", line)
# Find vertex line
if line[0] == 'v' and line[1] != 't' and line[1] != 'n': self.verts.append([dat[1],dat[2],dat[3]])
# Find polygon line
if line[0] == 'f': self.polys.append([dat[1],dat[2],dat[3]])
# Find section line
if line[0] == 'g': self.sections[len(self.polys)] = dat[1]
# Compute the normals for each polygon and each vertex
def computeNorms(self):
# Compute norms for each polygon
for p in self.polys:
v12 = [float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][0]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][0]),\
float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][1]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][1]),\
float(self.verts[int(p[1])-1][2]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][2]) \
]
v13 = [float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][0]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][0]),\
float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][1]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][1]),\
float(self.verts[int(p[2])-1][2]) - float(self.verts[int(p[0])-1][2]) \
]
# Compute poly normal
polynorm = self.cross(v12,v13)
norm = self.normalize(polynorm)
# Files created by OpenFX, Crossroads combination need have their normals flipped
if self.flip:
norm[0] = -norm[0]
norm[1] = -norm[1]
norm[2] = -norm[2]
# Append poly norm to polygonal norm array
self.pnorms.append(norm)
# Add norm to each vertexes norm..
try:
self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][0]) + norm[0],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][1]) + norm[1],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1][2]) + norm[2]
]
except:
self.vnorms[int(p[0])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]]
try:
self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][0]) + norm[0],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][1]) + norm[1],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][2]) + norm[2]
]
except:
self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]]
try:
self.vnorms[int(p[2])-1] = [float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][0]) + norm[0],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][1]) + norm[1],
float(self.vnorms[int(p[1])-1][2]) + norm[2]
]
except:
self.vnorms[int(p[2])-1] = [norm[0],norm[1],norm[2]]
# Average out each vnorm..
index = 0
for v in self.vnorms.values():
self.vavenorms.append([v[0]/4, v[1]/4, v[2]/4])
index += 1
# Utility function to normalize a given vector
def normalize(self,v):
mag = v[0]*v[0]+v[1]*v[1]+v[2]*v[2]
if mag <= 0:
mag = 1
else:
mag = math.sqrt(mag)
return [v[0]/mag, v[1]/mag,v[2]/mag]
# Utility cross product function
def cross(self,v1,v2):
x = 0
y = 1
z = 2
return [v1[y]*v2[z] - v1[z]*v2[y],\
v1[z]*v2[x] - v1[x]*v2[z],\
v1[x]*v2[y] - v1[y]*v2[x]
]
# Constructor
def __init__(self, file,translate=[0,0,0],flip=0):
self.verts = []
self.polys = []
self.pnorms = []
self.vnorms = {}
self.vavenorms = []
self.translate = translate
self.flip = flip
print "Read in file: "+str(file)
self.readOBJ(file)
print "Done reading in WFMesh, now compute norms"
self.computeNorms()
print "Done computing norms, now display WFMesh"
# Draw Function
def __call__(self):
glColorMaterial(GL_FRONT, GL_DIFFUSE);
glEnable(GL_COLOR_MATERIAL);
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
# Color Everything grey
glColor3f(0.5,0.5,0.5);
index = 0
glPushMatrix()
glTranslated(self.translate[0],self.translate[1],self.translate[2])
for p in self.polys:
glBegin(GL_POLYGON)
glNormal3f(float(self.pnorms[index][0]),float(self.pnorms[index][1]),float(self.pnorms[index][2]))
for i in range(0,len(p)):
glVertex3f(float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][0]),float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][1]),float(self.verts[int(p[i])-1][2]))
# Vertex Normals - not computed correctly, so commented out for now
# norm = self.vnorms[int(p[i])-1]
# glNormal3f(float(norm[0]),float(norm[1]),float(norm[2]))
glEnd()
index += 1
glPopMatrix()
cmd.extend("createWFObj", createWFObj)
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Torus.obj Torus.zip