This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "Ccp4 ncont"
m (18 revisions) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | {{Infobox script-repo |
| + | |type = script | ||
| + | |filename = ccp4_ncont.py | ||
| + | |author = [[User:Dalyte|Gerhard Reitmayr and Dalia Daujotyte]] | ||
| + | |license = GPL | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
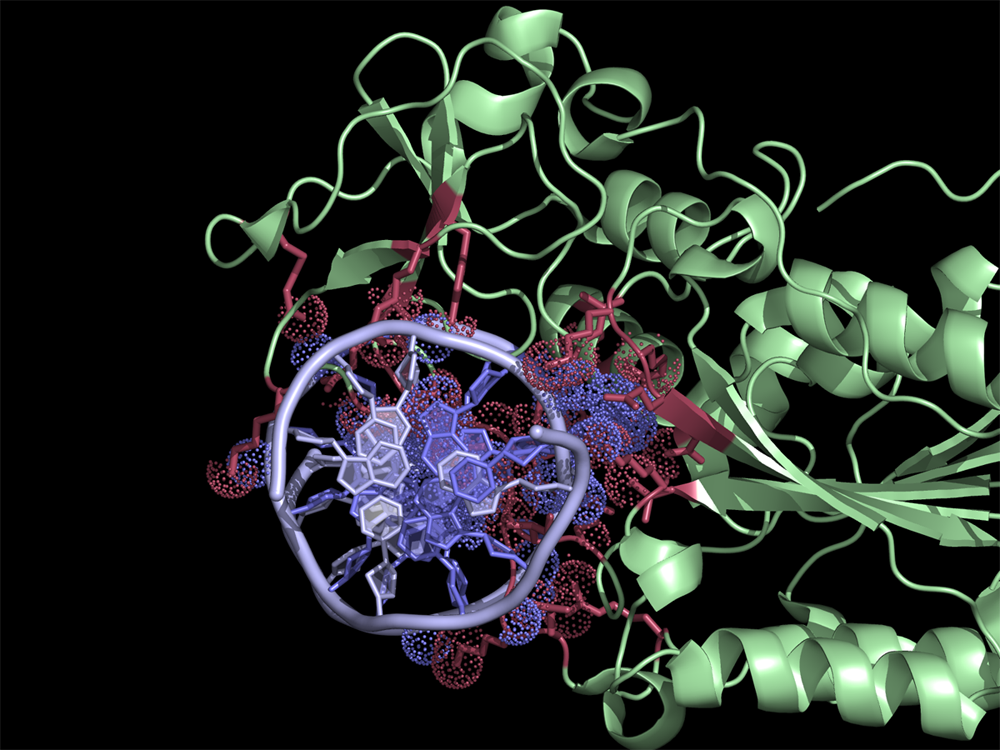
| + | [[File:HhaExample.png|thumb|300px|right|Interface residues (at cutoff <4A) in the 2c7r.pdb were found using NCONT. Usage of ccp4_ncont script in PyMOL allows easy selection of residues and atoms listed in ncont.log file. Interacting protein and DNA residues are colored in red and slate, respectively. Atoms in contact are shown in dots.]] | ||
The script selects residues and atoms from the list of the contacts found by NCONT from CCP4 Program Suite (NCONT analyses contacts between subsets of atoms in a PDB file). | The script selects residues and atoms from the list of the contacts found by NCONT from CCP4 Program Suite (NCONT analyses contacts between subsets of atoms in a PDB file). | ||
| − | First, we run NCONT on our pdb file to find interface residues. Then by using the | + | First, we run NCONT on our pdb file to find interface residues. Then by using the ccp4_ncont script in PyMOL we separately select residues and atoms listed in a ncont.log file. This generates two selections (atoms and residues) for each interacting chain, allowing quick manipulation of (sometimes) extensive lists in NCONT log file. |
| − | |||
| + | This script works best for intermolecular contacts (when NCONT target and source selections don't overlap). If crystal contacts (NCONT parameter cell = 1 or 2) are included then additional coding is required to distinguish inter from intramolecular contacts. | ||
| + | |||
== Usage == | == Usage == | ||
| − | + | ccp4_ncont( contactsfile, selName1 = "source", selName2 = "target" ) | |
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
| − | + | First use NCONT to find interface residues/atoms in the pdb file. Once you have ncont.log file proceed to PyMOL. | |
| − | + | Make sure you import the ccp4_ncont script first. | |
fetch 2c7r | fetch 2c7r | ||
| − | + | ccp4_ncont 2c7r.ncont, selName1=prot, selName2=dna | |
| + | |||
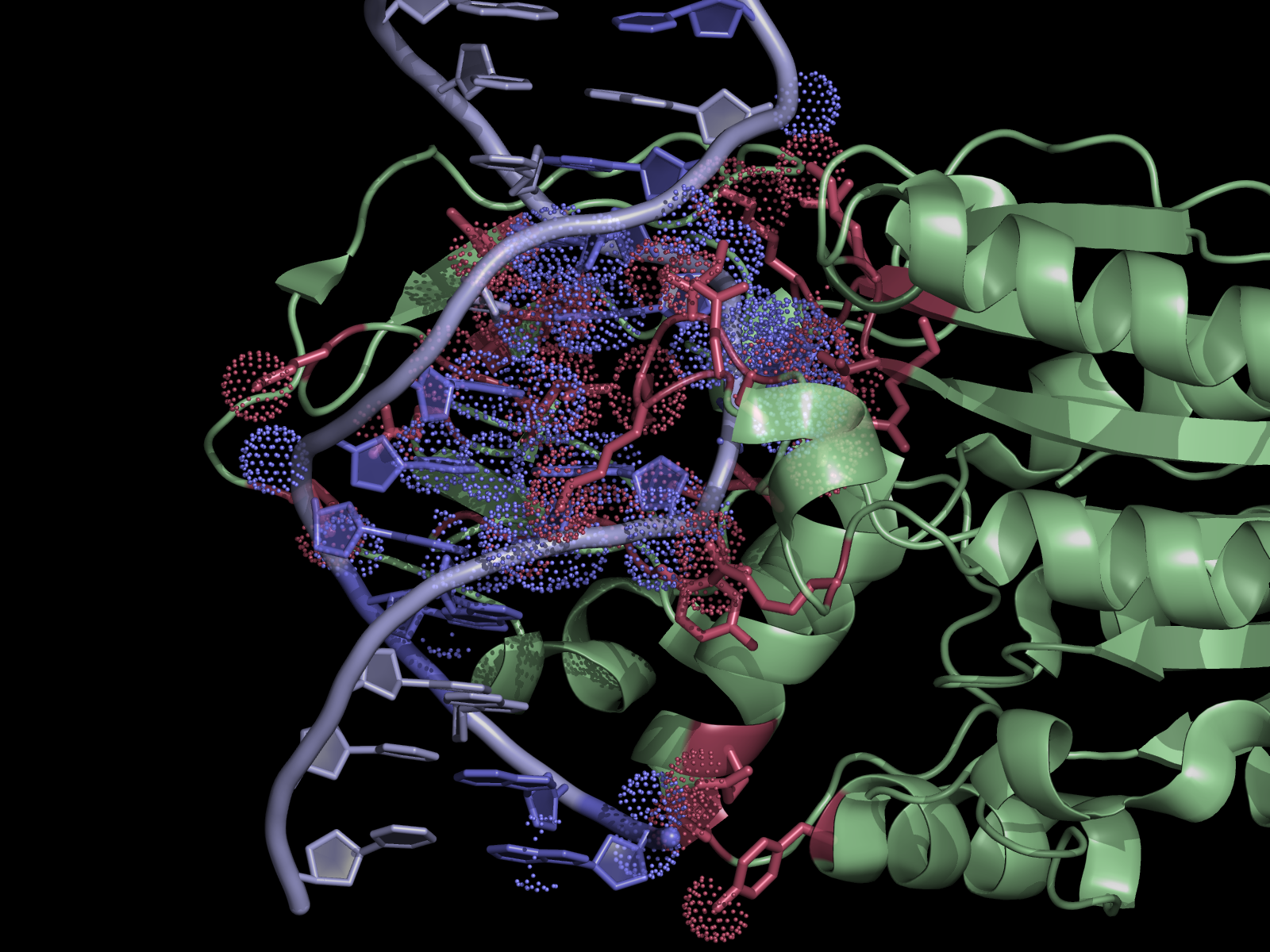
| + | [[File:HhaI20example.png|thumb|300px|right|Quick and easy selection of interacting residues and atoms listed in the NCONT log file. Protein and DNA residues are colored in red and slate, respectively. Atoms in contact are shown in dots.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template:PymolScriptRepoDownload|examples/ccp4_ncont_1.pml}} | ||
| + | <include src="https://raw.github.com/Pymol-Scripts/Pymol-script-repo/master/examples/ccp4_ncont_1.pml" highlight="python" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Getting a NCONT file == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Install CCP4 - for Linux === | ||
| + | Goto: http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/download.php <br> | ||
| + | Click: automated Downloads Pages <br> | ||
| + | Select: Linux, generic linux (x86) <br> | ||
| + | Select: Customized installation <br> | ||
| + | Select: Only CCP4 Program Suite, Executables -> Continue <br> | ||
| + | No additional packages -> Continue <br> | ||
| + | Download <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extract for example to: '''/home/YOU/Software/CCP'''4 <br> | ||
| + | Then run: <br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ /home/YOU/Software/CCP4/install.sh | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | write yes, read agreement, push y to agree license <br> | ||
| + | For sourcing scripts, say yes. <br> | ||
| + | See the changes to your environmental virables: <br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ less ~/.bashrc | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | === Use of NCONT - for Linux === | ||
| + | See here for the NCONT program and options: <br> | ||
| + | http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/html/ncont.html <br> | ||
| + | http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/html/pdbcur.html#atom_selection <br> | ||
| + | Locate the pdb, and now run in terminal: <br> | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="bash"> | ||
| + | $ ncont XYZIN 2c7r.pdb >> 2c7r.ncont << eof (#press enter) | ||
| + | > source A (#press enter) | ||
| + | > target C,D (#press enter) | ||
| + | > eof (#press enter, and now the program runs, and shell saves to 2c7r.ncont) | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Script_Library]] [[Category: | + | [[Category:Script_Library]] |
| + | [[Category:ThirdParty Scripts]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Structural Biology Scripts]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pymol-script-repo]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:06, 28 March 2014
| Type | Python Script |
|---|---|
| Download | ccp4_ncont.py |
| Author(s) | Gerhard Reitmayr and Dalia Daujotyte |
| License | GPL |
| This code has been put under version control in the project Pymol-script-repo | |
Overview
The script selects residues and atoms from the list of the contacts found by NCONT from CCP4 Program Suite (NCONT analyses contacts between subsets of atoms in a PDB file). First, we run NCONT on our pdb file to find interface residues. Then by using the ccp4_ncont script in PyMOL we separately select residues and atoms listed in a ncont.log file. This generates two selections (atoms and residues) for each interacting chain, allowing quick manipulation of (sometimes) extensive lists in NCONT log file.
This script works best for intermolecular contacts (when NCONT target and source selections don't overlap). If crystal contacts (NCONT parameter cell = 1 or 2) are included then additional coding is required to distinguish inter from intramolecular contacts.
Usage
ccp4_ncont( contactsfile, selName1 = "source", selName2 = "target" )
Examples
First use NCONT to find interface residues/atoms in the pdb file. Once you have ncont.log file proceed to PyMOL. Make sure you import the ccp4_ncont script first.
fetch 2c7r ccp4_ncont 2c7r.ncont, selName1=prot, selName2=dna
| Download: examples/ccp4_ncont_1.pml | |
| This code has been put under version control in the project Pymol-script-repo | |
<include src="https://raw.github.com/Pymol-Scripts/Pymol-script-repo/master/examples/ccp4_ncont_1.pml" highlight="python" />
Getting a NCONT file
Install CCP4 - for Linux
Goto: http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/download.php
Click: automated Downloads Pages
Select: Linux, generic linux (x86)
Select: Customized installation
Select: Only CCP4 Program Suite, Executables -> Continue
No additional packages -> Continue
Download
Extract for example to: /home/YOU/Software/CCP4
Then run:
$ /home/YOU/Software/CCP4/install.sh
write yes, read agreement, push y to agree license
For sourcing scripts, say yes.
See the changes to your environmental virables:
$ less ~/.bashrc
Use of NCONT - for Linux
See here for the NCONT program and options:
http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/html/ncont.html
http://www.ccp4.ac.uk/html/pdbcur.html#atom_selection
Locate the pdb, and now run in terminal:
$ ncont XYZIN 2c7r.pdb >> 2c7r.ncont << eof (#press enter)
> source A (#press enter)
> target C,D (#press enter)
> eof (#press enter, and now the program runs, and shell saves to 2c7r.ncont)