This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "AngleBetweenHelices"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (1 revision) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <gallery perrow= | + | {{Infobox script-repo |
| + | |type = Python Module | ||
| + | |filename = anglebetweenhelices.py | ||
| + | |author = [[User:Speleo3|Thomas Holder]] | ||
| + | |license = BSD | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Infobox psico | ||
| + | |module = psico.orientation | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery perrow=1 heights=191px widths=250px style="float:right; clear: right"> | ||
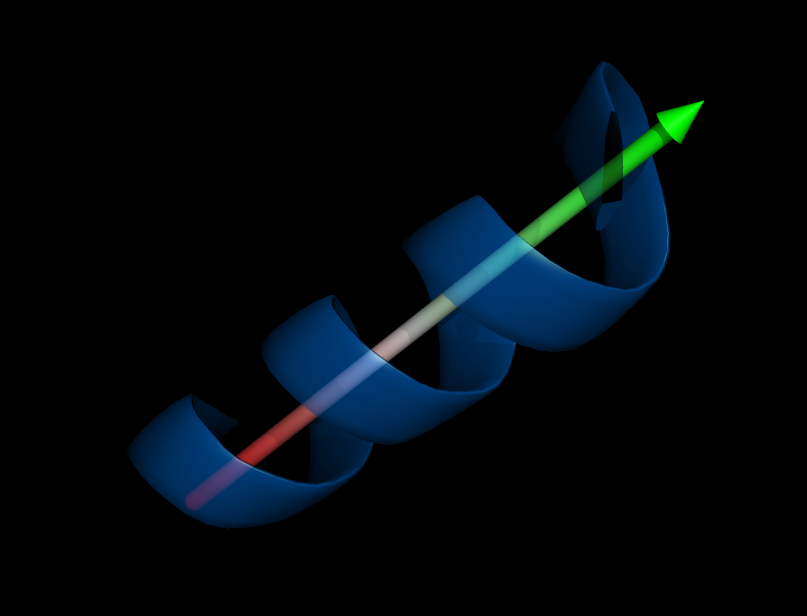
Image:Helix_orientation1.png|Orientation of a helix | Image:Helix_orientation1.png|Orientation of a helix | ||
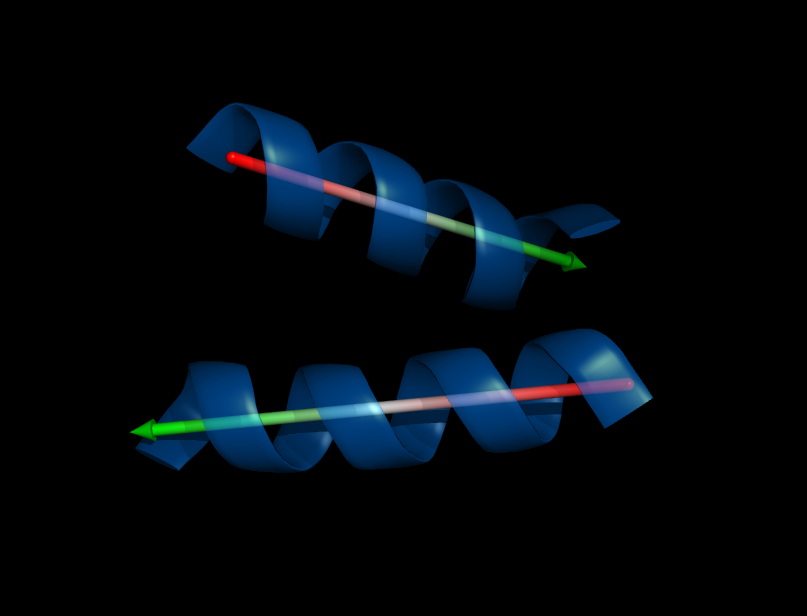
Image:Helix_orientation2.png|Orientation of two helices, their angle that separates the two is 145.08 degrees as reported by the script | Image:Helix_orientation2.png|Orientation of two helices, their angle that separates the two is 145.08 degrees as reported by the script | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
Calculate angle between alpha-helices or beta-sheets. | Calculate angle between alpha-helices or beta-sheets. | ||
There are four different methods implemented to fit a helix, two of them also work for sheets or loops. | There are four different methods implemented to fit a helix, two of them also work for sheets or loops. | ||
= Commands = | = Commands = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | angle_between_helices selection1, selection2 [, method [, visualize ]] | |
| − | + | helix_orientation selection [, visualize [, sigma_cutoff ]] | |
| − | + | helix_orientation_hbond selection [, visualize [, cutoff ]] | |
| − | + | loop_orientation selection [, visualize ] | |
| − | + | ||
| + | cafit_orientation selection [, visualize ] | ||
= Example = | = Example = | ||
| Line 50: | Line 61: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | = | + | == See Also == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [[angle_between_domains]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Structural_Biology_Scripts]] | [[Category:Structural_Biology_Scripts]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pymol-script-repo]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:54, 9 January 2017
| Type | Python Module |
|---|---|
| Download | anglebetweenhelices.py |
| Author(s) | Thomas Holder |
| License | BSD |
| This code has been put under version control in the project Pymol-script-repo | |
|
Included in psico | |
| Module | psico.orientation |
|---|---|
Calculate angle between alpha-helices or beta-sheets. There are four different methods implemented to fit a helix, two of them also work for sheets or loops.
Commands
angle_between_helices selection1, selection2 [, method [, visualize ]]
helix_orientation selection [, visualize [, sigma_cutoff ]]
helix_orientation_hbond selection [, visualize [, cutoff ]]
loop_orientation selection [, visualize ]
cafit_orientation selection [, visualize ]
Example
import anglebetweenhelices
fetch 2x19, async=0
select hel1, /2x19//B/23-36/
select hel2, /2x19//B/40-54/
# just calculate/visualize orientation of single alpha-helix
helix_orientation_hbond hel1
# get angle between two helices
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=1
angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=2
# get angle between beta-sheets
select sheet1, A/47-54/
select sheet6, A/146-149/
angle_between_helices sheet1, sheet6, method=loop_orientation
angle_between_helices sheet1, sheet6, method=cafit_orientation
Output:
PyMOL>angle_between_helices hel1, hel2, method=cafit_orientation
Using method: cafit_orientation
Angle: 145.08 deg