This is a read-only mirror of pymolwiki.org
Difference between revisions of "Stereo ray"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
png big-left-image.png | png big-left-image.png | ||
| − | == | + | == Example == |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang="python"> | |
| − | + | import stereo_ray | |
| − | + | stereo_ray output, 1000, 600 | |
| − | < | + | stereo_ray MyImages.png |
| − | + | </syntaxhighlight> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
This will create to images, one with an L and one with an R suffix. Just paste the two images next to each other (in some image editing program) and you're done. | This will create to images, one with an L and one with an R suffix. Just paste the two images next to each other (in some image editing program) and you're done. | ||
| − | + | == Python Code == | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Template:PymolScriptRepoDownload|stereo_ray.py}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Script_Library|Stereo Ray]] | [[Category:Script_Library|Stereo Ray]] | ||
| + | [[Category:UI_Scripts]] | ||
Revision as of 23:06, 7 December 2011
Manually
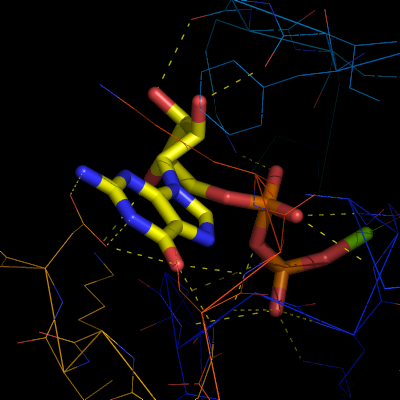
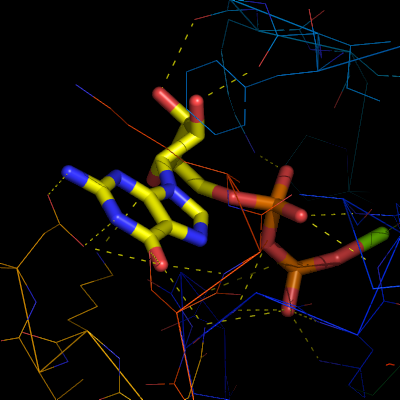
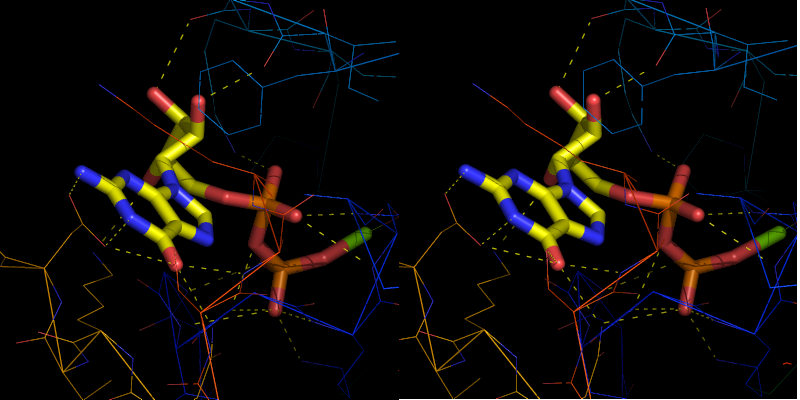
To get a stereo diagram you need two images. The left image is rotated +3 degrees and the right image is rotated -3 degrees.
To obtain the left image, type:
ray angle=+3 png left-image.png
Likewise, to obtain the right image, type:
ray angle=-3 png right-image.png
You still use any other ray based modifications, such as:
ray 1600,1200,angle=+3 png big-left-image.png
Example
import stereo_ray
stereo_ray output, 1000, 600
stereo_ray MyImages.png
This will create to images, one with an L and one with an R suffix. Just paste the two images next to each other (in some image editing program) and you're done.
Python Code
| Download: stereo_ray.py | |
| This code has been put under version control in the project Pymol-script-repo | |